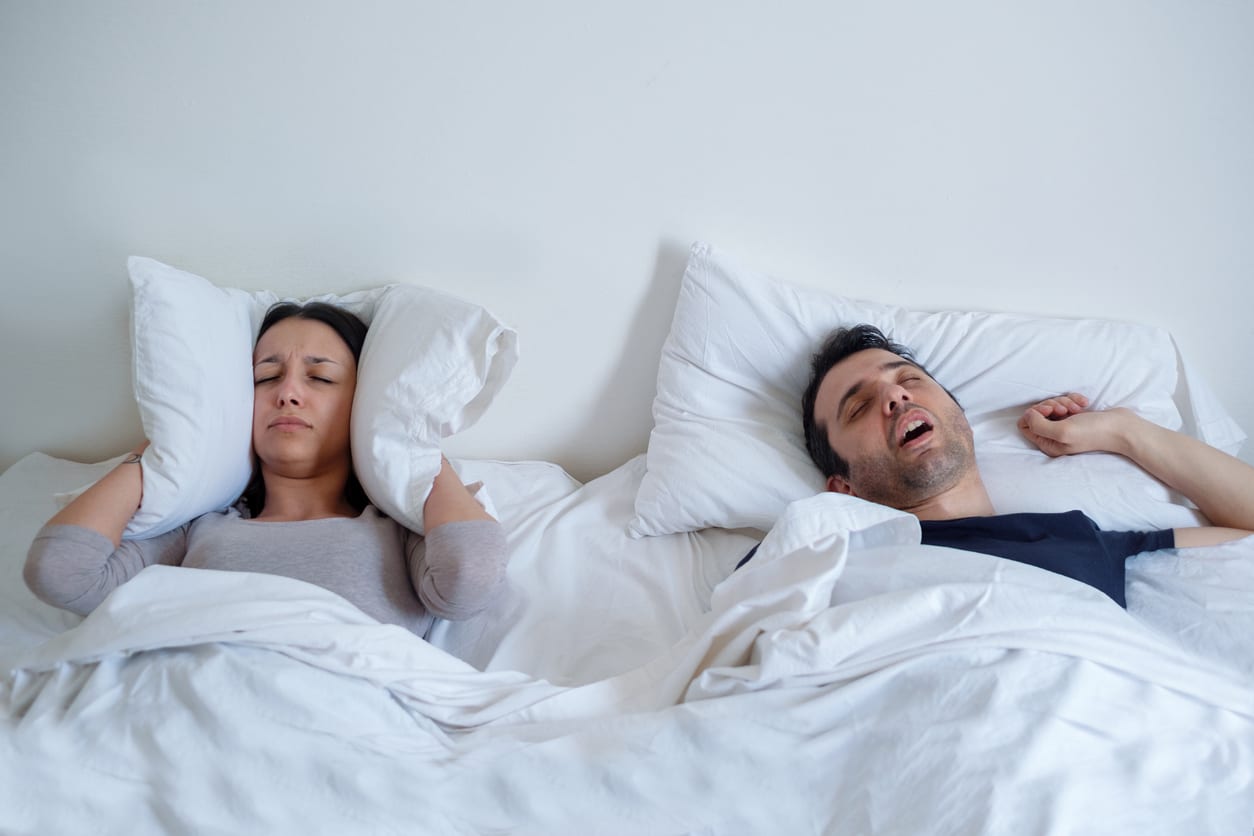
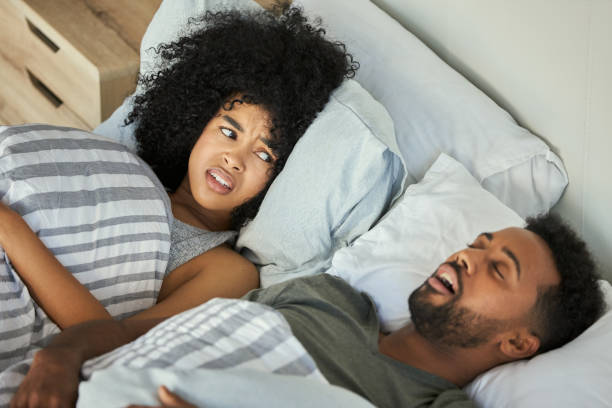
Stopping breathing for brief durations during sleep is a symptom of sleep apnea. Sleep apnea sufferers have oxygen deprivation throughout their sleep. Many people who stop breathing in their sleep don’t realise they have done so and continue to think they are having a regular sleep cycle. Snoring is a common misdiagnosis of sleep apnea.
In addition to making you groggy in the morning, sleep apnea symptoms has been linked to a host of other health problems. This sleep disorder raises the risk of heart failure, memory loss, and poor immunological function if left untreated. It can also provoke mental health problems.
Devices to assist breathing, medicine, and surgery are the most often used therapies. Alterations to one’s routine and the provision of basic amenities at home can, nevertheless, have a positive effect on one’s well-being and rest.
Wearing a CPAP mask at night is one of the most common treatments for sleep apnea. In spite of its efficacy, this approach might be unsettling for some. The same effects might be achieved with some home treatments. Here are six non-conventional approaches of treating sleep apnea.

Using Magnesium to Improve Your Sleep
Magnesium deficiency was detected in a study of persons with sleep apnea. There was a correlation between the elevated c-reactive protein and the decreased magnesium levels. The liver secretes C-reactive proteins, which are involved in the body’s fight against inflammation.
High oxidative stress is a nighttime problem for those with sleep apnea. Magnesium’s powerful anti-inflammatory effects may make it beneficial for persons with sleep apnea by lowering inflammation.
Avocados, seeds and nuts, bananas, and dark leafy greens like kale, spinach, and collard greens are all good sources of magnesium. Magnesium may be found in even the darkest of chocolates.
Supplemental magnesium may be helpful, but it’s always best to check with your doctor before adding anything new to your diet, especially if you have a medical history or are on medication.
Epsom salt baths before night are another way to raise magnesium levels in the body. The relaxing heat of a bath is also great for winding down for the night.

Keeping Your Weight In Check.
Losing weight is a regular recommendation made by doctors for patients suffering from sleep apnea. Upper-body obesity is associated with an increased risk of airway blockage and small nasal passageways. These blockages might result in a person’s abrupt and prolonged cessation of breathing during sleep.
You may alleviate your sleep apnea symptoms and keep your airways clean by sticking to a healthy weight. Obese persons can avoid upper airway surgery and prolonged CPAP therapy if they lose even a minor amount of weight, according to data from an Air Liquide healthcare source.
Sleep apnea can be cured in some people by losing weight. However, the problem may recur if the weight is regained.
Try Yoga.
Exercising regularly has been shown to boost energy, strengthen the heart, and alleviate sleep apnea. Practicing yoga can help you breathe better and easier.
Hypoxemia is more common in those who suffer from sleep apnea. Through a series of controlled breathing movements, yoga helps increase oxygen levels in the body. Therefore, practising yoga might lessen the number of times you wake up during the night.
Try a new sleeping posture
Even though it’s a simple adjustment, changing your sleeping posture can help you get better sleep and lessen the effects of sleep apnea. Over 50% of obstructive sleep apnea cases are reliant on posture, according to a research conducted in 2006. Sleeping in a supine (lying on one’s back) position has been linked to an exacerbation of symptoms. Some individuals find that switching to a side position while sleeping aids in regaining their regular breathing.
Air Liquide healthcare, however, has discovered that sleeping on one’s back is most beneficial for youngsters with sleep apnea. Make an appointment with your doctor to discuss your sleep apnea symptoms and how your body placement can affect your therapy.
Invest in a humidifier.
Humidifiers are machines that saturate the air with moisture. Air that is too dry might aggravate the respiratory system and cause other discomforts. Using a humidifier can help you breathe easier by loosening mucus and opening up your airways.
Essential oils like lavender, peppermint, and eucalyptus can be added to a humidifier for further advantages. These three oils are well-known for their ability to reduce inflammation and bring about a sense of calm.
Make sure to clean your humidifier in accordance with the guidelines provided by the manufacturer. They may serve as a breeding ground for germs and mould.
Don’t take alcohol or smoke
Modifying your way of life can have positive effects on your health, including improved sleep. If you want to lessen the impact of sleep apnea on your life, you should think about cutting down on tobacco and alcohol use.
The muscles in your throat regulate your breathing, and alcohol causes them to relax. It’s possible that this causes sleep disruptions and snoring. Inflammation of the airways, preventing normal breathing, is another possible outcome.
Tobacco usage, like alcohol consumption, can irritate and inflame the airways. The effects of snoring and sleep apnea may become more severe.
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of sleep apnea by several studies. The study found that treating sleep apnea might aid in smoking cessation since those with sleep apnea may be more likely to be smokers.
Make use of dental aids
Sleep apnea can be treated with an oral device by moving the jaw or tongue to keep the airway open. Mandibular advancement devices and tongue stabilisation devices are the two main types. These help by bringing the tongue or lower jaw forward, making space in the back of the throat.
People with sleep apnea who have difficulty using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine are encouraged to try an oral appliance instead, according to a set of recommendations published in 2015.
Due to the potential for more precise jaw alignment, custom-fit appliances are recommended in this recommendation over over-the-counter alternatives.

Raw honey is a great way to calm a sore throat.
Raw honey has been used medicinally for centuries, if not millennia, to ease the discomfort of a cough, ease swelling in the throat, and lessen the frequency and intensity of coughing fits.
Honey isn’t a drug, but its high concentration of phenolic chemicals makes it effective against inflammation. Its relaxing effects on the throat are especially welcome to those who suffer from sleep apnea.
Take one spoonful of raw honey dissolved in a cup of warm water or tea and consume it before bed. Since processed honey typically contains less minerals and antioxidants and also additional sugar, we advise going with raw, unpasteurized honey instead.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea symptoms can be alleviated with the help of assured home treatments and adjustments in way of life. Traditional methods of care shouldn’t be overlooked also. Medication and, in extreme cases, surgery are required methods of treatment. Contact Air Liquide Healthcare sleep specialist to know more
Before beginning any alternative therapy, it is recommended that you speak with your doctor. Worsening symptoms warrant prompt medical treatment.